Inside the 11th-hour passage of the bill elevating the U.S. antisemitism envoy
Concerted efforts from Sen. Jacky Rosen and outside groups helped push the long-delayed measure through a divided Congress

Courtesy
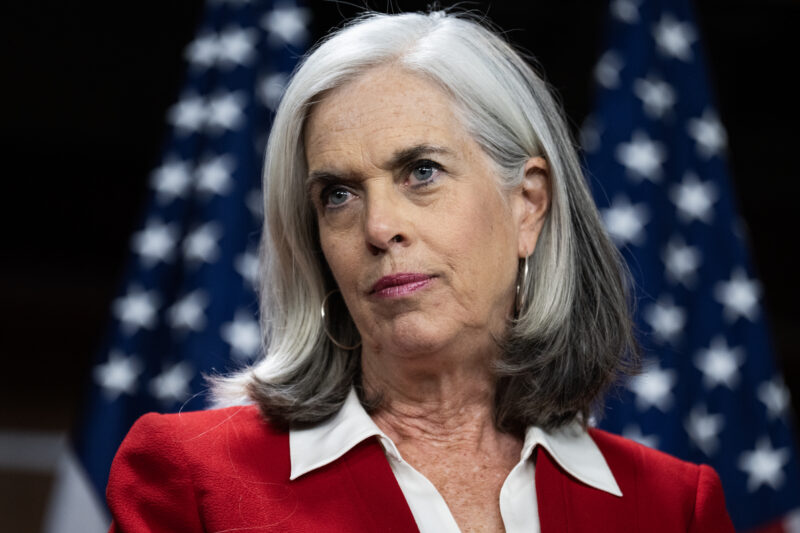
Sen. Jacky Rosen
A bill elevating the State Department’s special envoy to monitor and combat antisemitism to the rank of ambassador passed Congress on Thursday, nearly two years after first being introduced. Prior to its passage, the legislation appeared to stall in the Senate, raising concerns in the final days of the 116th Congress that legislators might have had to start over in the new Congress.
The House of Representatives first passed its version of the bill on Jan. 11, 2019. But — despite broad bipartisan support for the legislation — procedural issues bogged down the bill once it reached the Senate.
Several proponents of the bill both inside and outside Congress told JI that they believed the bill was going to die in the Senate, forcing a reset in the new session of Congress, which began January 3. This characterization was disputed by other Hill staffers and activists who had been communicating with senators to advance the legislation.
“I wouldn’t say it was dead, but it needed outside help,” a Republican aide told JI.
The bill was hampered by a dispute over whether to pass an amended version of the House bill or an identical bill that originated in the Senate, according to two Senate aides familiar with the bill, as well as American Jewish Congress President Jack Rosen.
Rosen, who spoke to several senators in an effort to move the bill forward, said Foreign Relations Committee ranking member Sen. Bob Menendez (D-NJ) preferred to pass the bill as a Senate measure. Menendez did not respond to a request for comment.
Backers of the legislation told JI that Sen. Jacky Rosen (D-NV) was critical to clearing the roadblocks that stood in the way of the bill’s passage.
“Rosen became incredibly engaged and helpful,” a Senate Republican aide familiar with the bill told JI. Both Senate staffers familiar with the bill said that the senator had aggressively pushed colleagues to pass the legislation.
“Senator Rosen… moved this up in her agenda and began to push her colleagues,” Karen Barall, director of government relations for Hadassah, told JI. “She was very effective in ensuring this was understood to be an important measure. Without her, this would not have passed the Senate.”
Rosen told JI she was pleased that the bill passed through both chambers by unanimous consent — a procedure used to expedite legislation without requiring a formal vote. “In the Senate, I was able to build on my bipartisan record of working with colleagues to fight antisemitism by ensuring this critically important bill was brought to the floor and passed,” she said.
The Senate passed the bill on December 16, leaving a narrow window for the House to pass the amended bill and send it to the president’s desk before the end of the 116th Congress.
To ensure the bill made it through the House, supporters had to contend with a chamber focused on urgent debates over government funding and COVID-19 relief payments, as well as disputes between Republican and Democratic leadership, generating concerns that the bill would not make it back through the House before the end of session.
“The issue that came up was not a substantive issue related to the text of the legislation, but rather they got caught up in Republican and Democratic food fight over other issues,” a pro-Israel activist involved in discussions about the bill said.
In addition to Rosen and the bill’s lead sponsors in the House, Reps. Chris Smith (R-NJ) and Brad Schneider (D-IL), a number of Jewish advocacy organizations joined the effort, including the Anti-Defamation League, Hadassah, the Orthodox Union, American Jewish Congress, American Jewish Committee, Jewish Federations of North America and the Conference of Presidents of Major American Jewish Organizations.
“After the Senate voted, there was very little time for the House leadership to act and major legislation — the NDAA, the omnibus, COVID relief — were understandably top priorities for House leadership,” said Barall. “Hadassah and other organizations made an aggressive push to get this done though, and send the bill to the president.”
The pro-Israel activist who asked not to be named credited Smith and Schneider for winning the support of their respective parties’ leaders to allow the bill to pass by unanimous consent on December 31.
Assuming President Donald Trump signs the bill, President-elect Joe Biden will become the first president to nominate a special envoy on antisemitism for Senate confirmation, although it will likely take time before he announces a pick for the spot, and even longer for the nominee to be confirmed.
Trump took 23 months to nominate the current special envoy, Elan Carr, for the position. An individual involved in discussions over the bill told JI that he expects an extended delay to fill the slot, noting that Senate-confirmed nominees face a more expansive background check process, and must go through the lengthy confirmation process, which can take months.
Given that Biden still has yet to nominate some Cabinet secretaries and a range of other high-level appointees that will require Senate confirmation, it’s unlikely the president-elect will name his pick for the position before his inauguration on January 20, the source added.
Among the names said to be under consideration by the Biden transition team are former ADL national director Abe Foxman, past envoy Ira Forman, Emory University professor and noted Holocaust historian Deborah Lipstadt, University of California, Berkeley professor Ethan Katz and ADL senior vice president of international affairs Sharon Nazarian. Foxman and Katz declined to comment to JI. Lipstadt did not respond to a request for comment.
Nazarian confirmed to JI she has spoken to members of the Biden transition team about the role and is submitting a formal application. She posited that her experience at ADL, as well as her personal experiences as an Iranian-born Jew, uniquely qualify her to expand and advance the special envoy’s office.
“My number one mission every day… is to advocate and to monitor and to educate, and to train as many people, stakeholders, government officials, as I can to first of all, make them aware of the threat of global antisemitism, and how it manifests in our lives today,” Nazarian said. “I feel like I’m well-positioned both as a practitioner of this work, as someone who’s led a very large team at ADL at the senior executive level, and also [as] someone who’s lived it through my own intersectional identity.”
Nazarian argued that the special envoy’s office, to date, has not taken a sufficiently modern or forward-looking approach to antisemitism, and has relied too heavily on 20th-century understandings of and approaches to global antisemitism.
Forman, who served as special envoy under former President Barack Obama from 2013 to the end of Obama’s term, declined to say if he was in consideration for the slot, but told JI, “I know there are a number of highly qualified people who could undertake this critical work and I am confident the Biden team will make an excellent choice.”